Abstract
Introduction: Surface display of proteins on Bacillus subtilis has emerged as a promising strategy in vaccinology, leveraging its safety, gastrointestinal resilience, and capacity for efficient antigen presentation. Targeting Staphylococcus aureus, a pathogen reliant on alpha-toxin (Hla) for virulence, this study focuses on a detoxified variant, HlaH35LH48L, to potentially neutralize toxicity while preserving immunogenicity. We investigated B. subtilis as an oral vaccine vector to display HlaH35LH48L and elicit mucosal and systemic immune responses in mice.
Methods: The hlaH35LH48L gene was fused to the yhcR anchoring motif and integrated into the amyE locus of B. subtilis HT800F via double-crossover recombination, generating strain BsHT2315. Successful chromosomal integration was confirmed by PCR. Surface display of HlaH35LH48L was verified through Western blot and bacterial-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (bactELISA). Swiss mice were orally administered BsHT2315, wild-type B. subtilis, or PBS (control). Serum IgG and intestinal IgA levels were quantified by ELISA.
Results: Western blot and bactELISA confirmed robust surface expression of HlaH35LH48L on BsHT2315. Oral immunization with BsHT2315 induced a significant two-fold increase in intestinal IgA compared to controls (p < 0.05), indicative of mucosal immunity. Serum IgG levels also showed a modest but significant elevation (1.5-fold, p < 0.01), suggesting systemic response activation.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated the successful development of B. subtilis BsHT2315 as an oral vaccine vehicle for HlaH35LH48L delivery. The strain triggered potent mucosal and systemic antibody responses, underscoring B. subtilis’s potential for cost-effective, needle-free vaccine platforms. Future work will explore protective efficacy against Staphylococcus aureus infection and scalability for clinical translation.
Introduction
Gram-positive bacteria serve as highly effective hosts for surface protein display due to their structural and functional adaptability. Their permeable cell surfaces facilitate the anchoring of heterologous proteins with extended amino acid chains1. A single cytoplasmic membrane streamlines polypeptide translocation, while the thick peptidoglycan layer imparts resilience against environmental stressors2. Furthermore, their robust cell wall architecture supports diverse laboratory manipulations and practical uses, including oral delivery systems, positioning Gram-positive species as versatile platforms for biotechnological and medical applications. Among protein anchoring mechanisms, sortase-mediated covalent linkage is the most well-characterized3, 4. Sortases, extracellular transpeptidases, cleave a conserved C-terminal LPXTG motif in target proteins, forming a transient acyl-enzyme intermediate that covalently attaches the protein to the peptidoglycan layer5. In biotechnological applications, foreign proteins are engineered for surface display by fusing an N-terminal signal peptide and a C-terminal cell wall anchoring domain (CWAD). CWADs typically feature three critical elements5: (i) a hydrophobic transmembrane domain, (ii) a positively charged tail to retain polypeptides intracellularly, and (iii) a pentapeptide sorting signal (e.g., LPXTG, where X is any residue) that serves as a sortase substrate, enabling enzymatic cleavage and passenger domain translocation.
Bacillus subtilis, a Gram-positive model organism in biotechnology, is widely recognized for efficient surface protein display. In B. subtilis, the YhcS sortase and its cognate substrate YhcR mediate covalent attachment of heterologous proteins to peptidoglycan6. Unlike the canonical LPXTG motif, YhcR harbors an atypical LPDTS sorting signal6. Remarkably, despite this divergence, YhcR retains 5′-nucleotidase activity—a trait commonly linked to LPXTG-bearing proteins in other species7. Prior work demonstrated that a YhcR-α-amylase fusion protein, processed by YhcS, achieves robust surface display6, suggesting that YhcR’s sorting sequence can direct heterologous protein anchoring. As a Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) organism capable of surviving in harsh environments, including the gastrointestinal tract, B. subtilis holds promise for oral vaccine delivery. However, YhcR remains underexplored for antigen presentation, motivating this study’s focus on exploiting YhcR to immobilize a mutant Staphylococcus aureus antigen on B. subtilis cell walls.
Staphylococcus aureus, a commensal bacterium colonizing human skin and nasal passages, causes infections ranging from mild (e.g., skin abscesses) to life-threatening (e.g., endocarditis, bacteremia, and toxic shock syndrome)8. The rise of multidrug-resistant strains and the pathogen’s multifactorial virulence complicate treatment and vaccine development9. Alpha-toxin (Hla), a pore-forming cytolytic protein expressed by ~83% of pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus isolates10, disrupts host barriers by lysing eukaryotic cells11, 12. Structural studies identified HlaH35L—a hemolytically inactive mutant with a histidine-to-leucine substitution at position 35—as a protective antigen in murine models of acute infection13, 14. To prevent potential reversion, a second mutation (H48L) was introduced, yielding the double mutant HlaH35LH48L as a stable toxoid15.
In this study, we engineered a novel B. subtilis strain displaying HlaH35LH48L on its surface via YhcR-mediated anchoring. Oral immunization of mice with this strain elicited elevated serum IgG and intestinal IgA titers, suggesting its potential as an oral vaccine platform. These findings underscore the utility of B. subtilis-YhcR for antigen delivery and warrant further investigation into mucosal immunization strategies.
Methods
Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
The bacterial strains used in this study were Escherichia coli OmniMAX™ (Invitrogen) for cloning and Bacillus subtilis HT800F16 as an expression host. Competent cell preparation for both E. coli and B. subtilis followed established protocols17, 18. Cells were cultured in LB medium supplemented with antibiotics (100 µg/mL ampicillin for E. coli or 10 µg/mL chloramphenicol for B. subtilis) at 37°C with shaking. All plasmids and strains are listed in Table 1.
| Plasmids / Strains | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| pHT2328 | Template plasmid used to obtain the hla H35LH48L gene | Our lab’s stock |
| pHT1796 | The integration vector contains Pgrac100-MCS-yhcR118 and amyE locus, used as the backbone | Our lab’s stock |
| pHT2315 | The integration vector contains Pgrac100-hla H35LH48L -yhcR118 and amyE locus | This study |
| BsHT1796 | B. subtilis strain with the integration of Pgrac100-MCS-yhcR118 into the chromosome at the amyE locus, used as the control | Our lab’s stock |
| BsHT2315 | B. subtilis strain integration of Pgrac100- hla H35LH48L -yhcR118 into the chromosome at the amyE locus | This study |
| Primers | Oligonucleotide sequences (5’ – 3’) | Purpose | Amplicon length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ON2336 ON2335 | ACTGTCGCTTCCAAGACGTCGTTTGTCATTTCTTCTTTC AAAGGAGGAAGGATCCATGAAAAC | Amplify hla H35LH48L | 993 |
| ON2332 ON2335 | GATCTTCTTTAATTGGGTCTTCCGTCCCCGGATCATCTC AAAGGAGGAAGGATCCATGAAAAC | Colony PCR for E. coli | 1151 |
| ON469 ON2137 | GGCGTTCTGTTTCTGCTTCG CTGTTTGTGATGGTTATCATGCAGGATTG | Confirm integration at 5’amyE site | 1097 |
| ON925 ON2378 | GAATTAGCTTGGTACCAAAGGAGGTAAGGATCACTAG CTCAACTGTCGCTTCCAAGACG | Confirm the presence of yhcR-hla H35LH48L after integration | 1122 |
| ON2331 ON470 | GACGGAAGACCCAATTAAAGAAGATCCAAGGCCAGGTGAAG AACCCGCTCCGATTAAAGCTAC | Confirm integration at 3’amyE site | 1477 |
Plasmid and Strain Construction
To facilitate the anchoring of heterologous protein on the B. subtilis cell wall, the vector pHT1796, containing the yhcR sequence, was used as a template in the study. The target gene hlaH35LH48L was initially amplified from the synthesized plasmid pHT2328 using the primers ON2336 and ON2335, as detailed in Table 2. After digestion with the two restriction enzymes, BamHI and AatII, both the target gene and the template pHT1796 were ligated using T4 DNA ligase to construct the plasmid pHT2315. The ligated plasmid pHT2315 was transformed into E. coli OmniMAX™, and cells containing the plasmid were screened on LB agar plates supplemented with ampicillin. The constructed plasmid was subsequently confirmed via colony PCR and sequencing.
Following cloning, the fusion gene yhcR-hlaH35LH48L from pHT2315 was naturally transformed into the chromosome of B. subtilis HT800F. The resulting strain, in which the fragment was integrated through double crossover at the amyE locus, was designated as BsHT2315. Bacterial cells were screened on LB agar plates containing chloramphenicol, and colonies were further validated by PCR.
For each colony, three pairs of primers were used to ensure correct integration. Details of all primers, including their nucleotide sequences and binding sites, are provided in Table 2. All bacterial strains, including the newly constructed BsHT2315, were stored at −80°C for further analysis.
Expression in B. subtilis Vegetative Cells
The BsHT2315 bacterial cells encoding recombinant HlaH35LH48L were pre-cultured in 4 mL of LB broth supplemented with chloramphenicol until the OD600 reached approximately 2–3. The suspension cells were then sub-cultured into 10 mL of LB broth containing chloramphenicol and shaken at 37°C and 220 rpm until the OD600 reached 0.8. Next, the suspension was sub-cultured into 10 mL of LB medium and incubated at 37°C with shaking at 220 rpm until an OD600 of 0.8 was achieved. Subsequently, the culture was induced with IPTG at concentrations of 0 mM, 0.1 mM, and 1 mM and incubated for 20 hours at 30°C.
For Western blot preparation, cell pellets were collected by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 2 minutes. For whole-bacterial cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (bactELISA), the culture was collected with 30% glycerol added as a preservative. All samples were stored at -80°C.
Detection of HlaH35LH48L in recombinant B. subtilis strain by Western Blot
Pellets containing cell wall–bound proteins were incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes in 100 μL of lysis buffer (0.25 M sucrose, 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.2) supplemented with 3 μL of 50 mg/mL lysozyme. The samples were then combined with 5× loading buffer and heated at 95°C for 5 minutes. After separation by SDS-PAGE, proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane.
For Western blot analysis, reactive bands were detected using an anti-Hla primary antibody (raised in mice) at a dilution of 1:20,000, followed by incubation with a rabbit anti-mouse IgG–HRP conjugate (Sigma) at a dilution of 1:40,000. Signal detection was performed using Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The BsHT1796 strain and the attenuated toxin HlaH35LH48L were utilized as controls in the assay.
Confirmation of HlaH35LH48L cell wall surface display by bactELISA
Whole-bacterial cell ELISA (bactELISA) was employed to verify the anchoring of HlaH35LH48L on the B. subtilis cell wall. This technique was referenced in the study by Cumming et al.19. Briefly, BsHT1796 and BsHT2315 vegetative cells, serving as analytes, were resuspended in 200 μL of coating buffer (100 mM NaHCO3, pH 9.6) and directly coated onto a microplate (Thermo Scientific™ Nunc™ MicroWell™ 96-Well Microplates) overnight at 4°C. The samples were washed twice with 100 μL of 0.1% PBS-Tween and then incubated in blocking buffer, consisting of PBS-Tween supplemented with 5% (w/v) skim milk, at room temperature for 1 hour. After washing twice, 50 μL of anti-Hla primary antibody (diluted 1:10,000) was applied to each well and incubated for 2 hours at room temperature. Next, 50 μL of rabbit anti-mouse IgG–HRP conjugate (Sigma), diluted 1:40,000, was added. The plates were incubated with the conjugate for 2 hours at room temperature, washed, and then incubated with 50 μL of TMB Liquid Substrate for ELISA (Sigma) for 20 minutes. Finally, 50 μL of 1N HCl was added to stop the reaction. Absorbance was measured at OD450 using a BMG Labtech CLARIOstar plate reader. Each sample was replicated three times, and statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA test in GraphPad Prism software (USA).
Oral administration in mice
Each experimental group consisted of five 6-week-old female Swiss mice. Oral immunizations were administered on days 0, 14, and 28 using 250 µL of B. subtilis vegetative cells (strains BsHT1796 and BsHT2315) at an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 60, diluted in 1X PBS. The control groups comprised mice receiving either BsHT1796 or PBS via oral gavage. Blood and stool samples were collected on days 21, 35, and 42, while small intestine samples were collected on day 42. For analysis, 0.6 g of feces or small intestine tissue was treated with 500 µL of 1X PBS containing 0.2 mg/mL PMSF, homogenized, and centrifuged to obtain the supernatant.
Indirect-ELISA
A 96-well plate (Thermo Scientific™ Nunc™ MicroWell™) was coated with 50 μL of HlaH35LH48L protein (produced by our lab) at a concentration of 5 μg/mL. Subsequently, 50 μL of either serum, fecal, or intestinal extract, serving as the primary antibody, was added at dilutions of 1:250 for serum and 1:50 for fecal/intestinal extract, followed by overnight incubation at 4°C. The wells were then incubated with either anti-mouse IgG (whole molecule) peroxidase-conjugated antibody produced in rabbits (Sigma, A9044) at a dilution of 1:40,000 or anti-mouse IgA (α-chain specific) peroxidase-conjugated antibody produced in goats (Sigma, A4789) at a dilution of 1:10,000 for 2 hours. All samples were analyzed in triplicate, and absorbance at 450 nm (OD450) was measured using a CLARIOstar plate reader. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test in GraphPad Prism software (USA).
Results
Construction of vector pHT2315
The target gene hlaH35LH48L, with an expected size of 993 bp, was amplified from pHT2328 via PCR and subsequently fused with the C-terminal yhcR-encoding sequence of pHT1796, resulting in the construction of pHT2315. The structure of vector pHT2315 is illustrated in Figure 1A. Following transformation, E. coli colonies harboring the recombinant plasmids were selected on LB agar plates containing ampicillin, and colony PCR was performed. The colony PCR results revealed a band at 1151 bp (Figure 1B), confirming the presence of the fusion gene hlaH35LH48L-yhcR in pHT2315. The sequence of hlaH35LH48L-yhcR was further verified by DNA sequencing (data not shown).
Generation of recombinant BsHT2315 integrated yhcR-hlaH35LH48L fragment
The constructed vector pHT2315 was successfully delivered into Bacillus subtilis HT800F through the process of natural transformation. During the transformation, DNA uptake occurred in some bacterial cells, leading to the integration of the heterologous fusion gene hlaH35LH48L-yhcR into the B. subtilis chromosome at the homologous amyE locus. Bacterial cells that did not incorporate the target fusion gene were eliminated through a preliminary screening on chloramphenicol LB agar plates.
PCR analysis was performed on the newly generated strain to confirm the integration of the hlaH35LH48L-yhcR fusion gene into the B. subtilis chromosome via a double-crossover recombination event. This analysis employed three specific primer pairs with distinct functions: one pair verified the presence of the gene of interest, while the other two targeted the integration sites at the 3′ and 5′ ends of amyE, respectively (Figure 1C). Gel electrophoresis results showed visible bands of varying sizes for all colonies with the three primer pairs (Figure 1D), matching the predicted sizes as outlined in Table 2, thereby confirming the successful creation of the integrated strain. The newly engineered strain was designated BsHT2315.
Display of HlaH35LH48L on B. subtilis vegetative cell surface
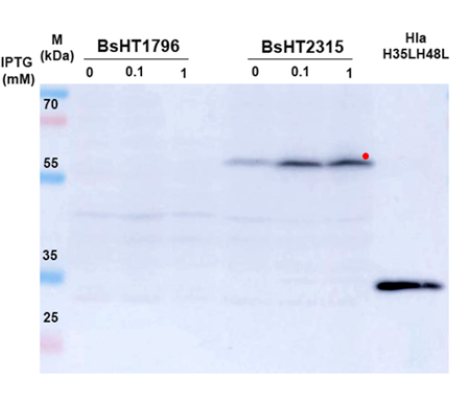
In this experiment, the vegetative cells of BsHT1796 and BsHT2315 strains were lysed after resuspension in a lysis buffer containing lysozyme. Proteins released from both strains, along with the control (purified Hla produced by our lab), were loaded onto an SDS-PAGE gel, separated, and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Western blot analysis was then conducted using a primary antibody raised in mice against Hla and a secondary rabbit anti-mouse IgG conjugated with HRP. Finally, the interaction between the ECL substrate and the HRP enzyme produced a chemiluminescent signal, visualizing the proteins on the membrane.
As shown in Figure 2A, compared to the BsHT1796 strain, which lacks the hlaH35LH48L protein-encoding gene, BsHT2315 under inducible conditions with 0.1 and 1 mM IPTG displayed visible bands of relatively equal intensity. Meanwhile, the BsHT2315 sample without IPTG induction also exhibited a band, but of lighter intensity. The difference in band thickness corresponding to the inducer concentration indicated that expression of the target fusion protein was regulated by the correct Pgrac212 promoter and lacI operon system in the presence of the inducer. Additionally, the larger molecular size of the fusion protein produced by the strain BsHT2315, compared to the purified HlaH35LH48L, is likely due to the contribution of the yhcR C-terminal region, which increased the molecular weight.
To confirm that HlaH35LH48L was anchored on the B. subtilis cell wall after being linked to YhcR, a bactELISA assay was performed. In this assay, only samples induced with 0.1 mM IPTG were evaluated. As antigens, B. subtilis vegetative cells were directly coated onto a microplate. Cells with target proteins anchored on the cell surface would subsequently bind to anti-Hla and secondary antibodies. The coated cells remained stable during a procedure that allowed them to retain their shape, clearly demonstrating the display of the fusion protein on the cell wall. Figure 2B demonstrated a significant two-fold increase in the signal intensity for HlaH35LH48L on the cell wall of BsHT2315 compared to the control (0.7260 ± 0.0074 vs. 0.3447 ± 0.0097, p = 0.0009). This indicated successful surface display of the target protein on the cell wall of B. subtilis.
IgG and IgA response by oral administration
We confirmed the successful surface display of alpha toxin on B. subtilis cells. To assess the immunogenicity of cell-surface displayed HlaH35LH48L and its oral delivery efficacy, Swiss mice were orally immunized with three doses of B. subtilis vegetative cells on days 0, 14, and 28. IgG and IgA antibody levels were evaluated in serum, fecal, and small intestinal samples.
ELISA results in Figure 3B revealed a significant increase in anti-HlaH35LH48L intestinal IgA levels in mice immunized with BsHT2315 cells on day 42 (OD450 = 0.135 ± 0.004, p = 0.0005), which was two-fold higher than those immunized with BsHT1796 (OD450 = 0.066 ± 0.008). Similarly, a significant difference (p = 0.0012) was observed between BsHT2315 and PBS groups (OD450 = 0.076 ± 0.017). As expected, no significant differences were observed between the two control groups (BsHT1796 and PBS), as BsHT1796 lacks the target protein sequence. There was no significant increase in fecal IgA levels in the BsHT2315 group compared to the control (data not shown). In addition, serum IgG levels of BsHT2315 exhibited a slight increase on days 21 (0.194 ± 0.030, p = 0.0239), 35 (0.164 ± 0.019, p = 0.8436), and 42 (0.203 ± 0.045, p = 0.0151) compared to the control group BsHT1796. However, no significant differences were observed between dosage regimens throughout the immunization process (Figure 3A).
These results suggest that B. subtilis cells displaying HlaH35LH48L on their surface via YhcR were successfully delivered to the mouse gut and elicited a local immune response at mucosal sites following oral administration.
Discussion
This research focused on generating a B. subtilis strain that displayed a staphylococcal alpha-toxin variant on its cell surface. Here, we successfully engineered plasmid pHT2315, containing the fusion gene hlaH35LH48L-yhcR. The constructed vector was designed to incorporate the gene of interest into the B. subtilis chromosome via double-crossover homologous recombination, ensuring stability and retention of the target gene even in the absence of selective pressure20, 21. This design could be advantageous for large-scale production, as the use of antibiotics is often a concern in biotechnological manufacturing. In addition, the host strain B. subtilis HT800F is a multiple-protease-deficient strain designed to prevent protein degradation and maintain stability in recombinant gene expression. Unlike other commonly used B. subtilis host cells, such as WB800 and WB800N, HT800F is free from repetitive DNA sequences, further enhancing its ability to maintain stable expression of target proteins22. Furthermore, the newly integrated strain BsHT2315 would express HlaH35LH48L under the control of the strong promoter Pgrac100, which enables robust protein expression in B. subtilis while suppressing background expression in E. coli23.
In this study, surface anchoring was facilitated by the interaction between the YhcS sortase enzyme and the YhcR motif fused to the target alpha-toxin. YhcS, predominantly expressed during the stationary phase6, recognized the YhcR sorting signal and catalyzed the covalent anchoring of the fusion protein HlaH35LH48L-YhcR to the peptidoglycan layer of the cell wall. By measuring the intensity of each band in Western blot analysis, we concluded that BsHT2315 samples induced with 0.1 mM and 1 mM IPTG exhibited high signal intensity. A slightly visible band was detected in the uninduced BsHT2315 sample (0 mM IPTG). This could be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the bacterial Lac repressor may not bind to the operator site with 100% efficiency, allowing for some basal transcription24. Secondly, read-through transcription from upstream promoters might contribute to the low-level expression25. However, the leaky expression in the uninduced BsHT2315 sample had a negligible impact on our experimental outcomes. Additionally, Lac repressor leakiness does not impact vaccine safety, as the target antigen is a mutant alpha-toxin specifically designed for safe handling15. Furthermore, the study primarily examined bacteria that had undergone induction and were actively displaying antigen. Overall, the Western blot and bactELISA results demonstrated that BsHT2315 successfully expressed alpha-toxin and that YhcR effectively anchored it to the bacterial cell wall.
The efficacy of oral vaccines can be compromised by various factors, including the harsh gastrointestinal environment, inefficient antigen presentation, and the risk of oral tolerance26. In this research, mice orally administered with BsHT2315 cells exhibited a two-fold increase in intestinal IgA levels compared to those administered with BsHT1796 or PBS. The presence of IgA in the intestines indicates that the vaccine has successfully interacted with the mucosal immune cells, triggering an immune response. However, fecal IgA levels may not show the same increase, suggesting that the immune response is localized to the intestinal mucosa and not fully reflected in the feces. Antigens delivered via the oral route interact with gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), including Peyer’s patches and M cells27. M cells transport antigens across the intestinal epithelium, where they are captured by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages27. While mucosal immunity primarily stimulates IgA production, some APCs migrate to systemic lymphoid organs, leading to systemic IgG induction27, 28. In this study, the slight increase in IgG levels in mouse serum may be due to the limited immune stimulation typically observed with oral vaccines, suggesting that repeated or higher doses may be necessary. A greater antigen dose could enhance mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) exposure to the target antigen, thereby strengthening systemic immune responses29. On the other hand, B. subtilis has been shown to be an effective adjuvant for oral vaccines30. A previous study reported that partial protection against lethal challenges was observed exclusively in mice orally immunized with recombinant B. subtilis strains, either as vegetative cells or spores, expressing intracellular Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin B subunit (LTB)31. Therefore, further optimization with no adjuvant needed may be required to ensure an adequate antigen dose for effective immunization with BsHT2315.
Staphylococcus aureus remains a significant public health threat, and there is currently no approved vaccine9. Alpha-toxin is a major virulence factor contributing to various Staphylococcus aureus infections. To date, there have been few studies utilizing B. subtilis cell surfaces as a platform for antigen expression31, 32, and the expression of alpha-toxin on this platform is investigated for the first time in this study. We have developed a novel B. subtilis strain capable of displaying alpha-toxin on its cell surface and effectively delivering it as an antigen to mice. This represents an initial step toward further research into B. subtilis cell surface display systems for potential vaccine applications.
Conclusion
This study successfully constructed the vector pHT2315, harboring the target fusion gene hlaH35LH48L-yhcR, and developed a novel strain, BsHT2315, capable of displaying heterologous proteins on the bacterial cell wall using the sorting signal YhcR. Furthermore, a significant increase in intestinal IgA levels was observed, demonstrating the potential of B. subtilis vegetative cells to deliver antigens via the oral route and induce antibody production in the intestinal mucosa of mice.
Abbreviations
ANOVA (Analysis of variance), APCs (Antigen-presenting cells), B. subtilis (Bacillus subtilis), bactELISA (Bacterial-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), CWAD (Cell wall anchoring domain), DCs (Dendritic cells), E. coli (Escherichia coli), ECL (Enhanced chemiluminescence), ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), GALT (Gut-associated lymphoid tissue), GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe), HRP (Horseradish peroxidase), IgA (Immunoglobulin A), IgG (Immunoglobulin G), IPTG (Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside), LB (Luria-Bertani medium), LTB (Heat-labile toxin B subunit), MALT (Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue), OD600 (Optical density at 600 nm), PBS (Phosphate-buffered saline), PCR (Polymerase chain reaction), PMSF (Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride), RT (Room temperature), S. aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), SDS-PAGE (Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), and TMB (3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine).
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted at the Center of Bioscience and Biotechnology of Ho Chi Minh University of Science and at the Institute of Malaria - Parasitology - Entomology in Ho Chi Minh City. Nhi NY Nguyen, was supported by the Domestic Master/PhD Scholarship Program of Vingroup Innovation Foundation.
Author’s contributions
HDN designed the study. NN and AN analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. HDN and TP revised the manuscript. NN carried out the cloning and strain generation. NN and LD carried out the sporulation. LD, NN, AN, TM carried out animal experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 108.06-2019.11.
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the National Institute of Malariology - Parasitology - Entomology in Ho Chi Minh city, signed on March 01, 2020.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
-
Samuelson
P.,
Gunneriusson
E.,
Nygren
P.A.,
Stahl
S.,
Display of proteins on bacteria. Journal of Biotechnology.
2002;
96
(2)
:
129-54
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Vollmer
W.,
Blanot
D.,
Pedro
M.A. de,
Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiology Reviews.
2008;
32
(2)
:
149-67
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Emidio
N. Braga,
Cheloha
R.W.,
Sortase-mediated labeling: expanding frontiers in site-specific protein functionalization opens new research avenues. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology.
2024;
80
:
102443
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Zou
Z.,
Ji
Y.,
Schwaneberg
U.,
Empowering Site-Specific Bioconjugations In Vitro and In Vivo: Advances in Sortase Engineering and Sortase-Mediated Ligation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English.
2024;
63
(12)
:
e202310910
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Marraffini
L.A.,
Dedent
A.C.,
Schneewind
O.,
Sortases and the art of anchoring proteins to the envelopes of gram-positive bacteria. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews : MMBR.
2006;
70
(1)
:
192-221
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Nguyen
H.D.,
Phan
T.T.,
Schumann
W.,
Analysis and application of Bacillus subtilis sortases to anchor recombinant proteins on the cell wall. AMB Express.
2011;
1
(1)
:
22
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Pallen
M.J.,
Lam
A.C.,
Antonio
M.,
Dunbar
K.,
An embarrassment of sortases - a richness of substrates?. Trends in Microbiology.
2001;
9
(3)
:
97-102
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Tong
S.Y.,
Davis
J.S.,
Eichenberger
E.,
Holland
T.L.,
Fowler
V.G.,
Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clinical Microbiology Reviews.
2015;
28
(3)
:
603-61
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Chand
U.,
Priyambada
P.,
Kushawaha
P.K.,
Staphylococcus aureus vaccine strategy: promise and challenges. Microbiological Research.
2023;
271
:
127362
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Tabor
D.E.,
Yu
L.,
Mok
H.,
Tkaczyk
C.,
Sellman
B.R.,
Wu
Y.,
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Is Conserved among Diverse Hospital Respiratory Isolates Collected from a Global Surveillance Study and Is Neutralized by Monoclonal Antibody MEDI4893. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy.
2016;
60
(9)
:
5312-21
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Bhakdi
S.,
Tranum-Jensen
J.,
Alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiological Reviews.
1991;
55
(4)
:
733-51
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Berube
B.J.,
Wardenburg
J. Bubeck,
Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin: nearly a century of intrigue. Toxins.
2013;
5
(6)
:
1140-66
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Menzies
B.E.,
Kernodle
D.S.,
Site-directed mutagenesis of the alpha-toxin gene of Staphylococcus aureus: role of histidines in toxin activity in vitro and in a murine model. Infection and Immunity.
1994;
62
(5)
:
1843-7
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Brady
R.A.,
Mocca
C.P.,
Prabhakara
R.,
Plaut
R.D.,
Shirtliff
M.E.,
Merkel
T.J.,
Evaluation of genetically inactivated alpha toxin for protection in multiple mouse models of Staphylococcus aureus infection. PLoS One.
2013;
8
(4)
:
e63040
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Tran
V.G.,
Venkatasubramaniam
A.,
Adhikari
R.P.,
Krishnan
S.,
Wang
X.,
Le
V.T.,
Efficacy of Active Immunization With Attenuated α-Hemolysin and Panton-Valentine Leukocidin in a Rabbit Model of Staphylococcus aureus Necrotizing Pneumonia. The Journal of Infectious Diseases.
2020;
221
(2)
:
267-75
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Phan
T.T.,
Hoang
N.D.,
Chủng vi khuẩn Bacillus subtilis HT800 có khả năng duy trì tính ổn định trong biểu hiện gen tái tổ hợp [Internet]. Vietnam patent VN103078. 2024 Jun 25 [cited 2025 Feb 20]. Available from: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=VN434940751.
.
-
Green
M.R.,
Sambrook
J.,
Sambrook
J.,
Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual.Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor (N.Y); 2012.
Google Scholar -
Smith
M.C.,
Molecular biological methods for bacillus. FEBS Letters.
1991;
287
:
227-227
.
-
Cumming
C.G.,
Ross
P.W.,
Poxton
I.R.,
McBride
W.H.,
Grouping of β-haemolytic streptococci by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Journal of Medical Microbiology.
1980;
13
(3)
:
459-61
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Heap
J.T.,
Ehsaan
M.,
Cooksley
C.M.,
Ng
Y.K.,
Cartman
S.T.,
Winzer
K.,
Integration of DNA into bacterial chromosomes from plasmids without a counter-selection marker. Nucleic Acids Research.
2012;
40
(8)
:
e59
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Middleton
R.,
Hofmeister
A.,
New shuttle vectors for ectopic insertion of genes into Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid.
2004;
51
(3)
:
238-45
.
View Article Google Scholar -
VN103078 Chủng vi khuẩn Bacillus subtilis HT800 có khả năng duy trì tính ổn định trong biểu hiện gen tái tổ hợp [Internet]. [cited 2024 Dec 5]. Available from: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/es/detail.jsf;jsessionid=E0643316ABEDD510C62F6B6AB55F79CE.wapp2nA?docId=VN434940751&_cid=P20-M16JVP-72257-19.
.
-
Phan
T.T.,
Tran
L.T.,
Schumann
W.,
Nguyen
H.D.,
Development of Pgrac100-based expression vectors allowing high protein production levels in Bacillus subtilis and relatively low basal expression in Escherichia coli. Microbial Cell Factories.
2015;
14
(1)
:
72
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Nielsen
B.L.,
Willis
V.C.,
Lin
C.Y.,
Western blot analysis to illustrate relative control levels of the lac and ara promoters in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education : A Bimonthly Publication of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
2007;
35
(2)
:
133-7
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Anthony
L.C.,
Suzuki
H.,
Filutowicz
M.,
Tightly regulated vectors for the cloning and expression of toxic genes. Journal of Microbiological Methods.
2004;
58
(2)
:
243-50
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Simerska
P.,
Moyle
P.M.,
Olive
C.,
Toth
I.,
Oral vaccine delivery\textemdashnew strategies and technologies. Current Drug Delivery.
2009;
6
(4)
:
347-58
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Kobayashi
N.,
Takahashi
D.,
Takano
S.,
Kimura
S.,
Hase
K.,
The Roles of Peyer's Patches and Microfold Cells in the Gut Immune System: Relevance to Autoimmune Diseases. Frontiers in Immunology.
2019;
10
:
2345
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Hase
K.,
Kawano
K.,
Nochi
T.,
Pontes
G.S.,
Fukuda
S.,
Ebisawa
M.,
Uptake through glycoprotein 2 of FimH(+) bacteria by M cells initiates mucosal immune response. Nature.
2009;
462
(7270)
:
226-30
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Lavelle
E.C.,
Ward
R.W.,
Mucosal vaccines - fortifying the frontiers. Nature Reviews. Immunology.
2022;
22
(4)
:
236-50
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Souza
R.D. de,
Batista
M.T.,
Luiz
W.B.,
Cavalcante
R.C.,
Amorim
J.H.,
Bizerra
R.S.,
Bacillus subtilis spores as vaccine adjuvants: further insights into the mechanisms of action. PLoS One.
2014;
9
(1)
:
e87454
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Paccez
J.D.,
Nguyen
H.D.,
Luiz
W.B.,
Ferreira
R.C.,
Sbrogio-Almeida
M.E.,
Schuman
W.,
Evaluation of different promoter sequences and antigen sorting signals on the immunogenicity of Bacillus subtilis vaccine vehicles. Vaccine.
2007;
25
(24)
:
4671-80
.
View Article Google Scholar -
Ghaedmohammadi
S.,
Ahmadian
G.,
The first report on the sortase-mediated display of bioactive protein A from Staphylococcus aureus (SpA) on the surface of the vegetative form of Bacillus subtilis. Microbial Cell Factories.
2021;
20
(1)
:
212
.
View Article Google Scholar
Comments
Article Details
Volume & Issue : Vol 12 No 4 (2025)
Page No.: 7286-7294
Published on: 2025-04-30
Citations
Copyrights & License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Search Panel
Pubmed
Google Scholar
Pubmed
Google Scholar
Pubmed
Google Scholar
Pubmed
Google Scholar
Pubmed
Google Scholar
Pubmed
Search for this article in:
Google Scholar
Researchgate
- HTML viewed - 399 times
- PDF downloaded - 120 times
- XML downloaded - 34 times
 Biomedpress
Biomedpress





